Aramid fiber is one of the high-performance man-made fibers, with excellent performance and wide application. Aramid fibers are long-chain polymer molecules composed of amide groups and aromatic rings or their derivatives, collectively called “aromatic polyamide fibers” or “aramid fibers” for short. The production and research of aramid fiber in the United States, Japan, Europe, and other countries are rapidly growing.
Table of Contents
Types of aramid fiber
Structurally, aramid fiber is divided into para-aramid (PPTA) and meta-aramid (PMIA).
Para-aramid (PPTA)
Para-aramid is made of phthaloyl chloride (TPC) and p-phenylenediamine (PPD) as polymerized monomers, dissolved and drawn, and the structure is arranged straight.
Meta-aramid (PMIA)
Meta-aramid is formed by polycondensation of isophthaloyl chloride (IPC) and m-phenylenediamine (MPD), and its structure is zigzag.
Characteristics of aramid fiber
Aramid fiber has the characteristics of high strength, high modulus, low density, and high abrasion resistance and exhibits excellent physical and chemical properties.
Because of the difference in structure, the performance and usage of the two are very different and correspond to different downstream applications.
Among them, para-aramid has high strength and modulus characteristics and is mainly used in fields that require high temperature-resistant bulletproof armor, optical cables, friction sealing materials, rubber products, and high-strength cables.
Meta-aramid has excellent high-temperature resistance, flame retardancy, and insulation and is mainly used in high-temperature protective clothing, electrical insulation, and high-temperature filtration.
Advantages of aramid fiber
Aramid fiber has advantages over carbon fiber and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene in terms of temperature resistance and elongation.
Compared with carbon fiber, aramid fiber has better tensile toughness. It can replace carbon fiber in fields with structural reinforcement and toughness, such as fiber optic cable-reinforced structure, tire reinforcement, etc.
Compared with ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, aramid fiber’s high-temperature resistance is better, and it has unique application advantages in personal protection that requires high-temperature resistance.

Aramid Fiber Industrialization
Aramid fiber was born in the 1960s during the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union and was first developed as an aviation material in the United States.
After the end of the Cold War, the transition from strategic military materials to civilian products was realized with the gradual application of aramid fiber in the civilian field.
DuPont Corporation of the United States was the first to realize the commercial application of aramid fiber worldwide. Since then, manufacturers such as AkzoNobel and Hearst in the Netherlands have gradually admitted the industrialization of aramid fibers.
Applications of aramid fiber
Optical fiber reinforcement
Para-aramid fibers are widely used in indoor and outdoor optical fiber and power cables, outdoor ADSS optical cables, indoor optical cables, and jumpers. They play a significant role in tensile reinforcement.
With the development of 5G communication, optical cables will gradually replace traditional metal wires as the primary medium for information transmission. Para-aramid fiber has become the ideal non-metallic reinforcement material for optical cables.
The construction of 5G communication networks has greatly accelerated the use of aramid fiber in the information field. As the key to the “new infrastructure,” the 5G network will promote the increase in the output of optical cables, thereby driving the continuous expansion of para-aramid use.
The global para-aramid market size is estimated to be US$3.7 billion in 2025, with a CAGR of 9.7%. It is estimated that 70% of the worldwide aramid optic fiber will be para-aramid in 2025, and the market space of para-aramid fiber will reach 3.7 billion US dollars. According to research and market forecasts, the demand for para-aramid and meta-aramid will reach 180,000 tons and 100,000 tons in 2025.
Aerospace and military applications
Initially, aramid fibers were used to manufacture rocket engine shells, aviation cylinders, and military products. However, as the requirements for aerospace materials became more stringent, the application of aramid fibers expanded to secondary structural materials, such as cabin doors, windows, fairing body surfaces, interior ceilings, partitions, bulkheads, luggage racks, and seats.
The light weight of aramid fiber is one of the main reasons it’s used extensively in aircraft. After using aramid fiber composite material, aircraft weight can be reduced by about 30%.
Civil field
Aramid fiber composite materials are mainly used in the civil field as reinforcing materials. For instance, reinforced cement with aramid fiber can obtain lightweight and high-strength structural parts, effectively preventing cement products’ cracking.
Additionally, aramid fiber is tough and can be processed into cloth, cable, etc., braided into a steel bar as a cement-reinforced skeleton material. This material is light in weight, high in strength, corrosion-resistant, and shear-resistant. Moreover, aramid fiber-reinforced adhesive laminated wooden beam technology reduces costs using low-grade wood instead of high-grade precious wood.
Transportation
Aramid fiber is mainly used to manufacture automobile or aircraft tires for transportation. The tire made of aramid fiber is light and thin, has low rolling resistance, good wear resistance, high bearing capacity, and is resistant to cutting and puncture.
The movement of the center of gravity is small during work, the steering performance is good, and the car rides comfortably. The heat dissipation is excellent, and the tire has a long service life, meeting the requirements of modern supersonic aircraft for using tires.
High-temperature filter material
Meta-aramid fibers have excellent thermal stability, making them difficult to age at high temperatures, and they can be used for a long time at 220°C. They are good in wear resistance and alkali resistance but poor in acid resistance.
Various filter materials made of meta-aramid have been widely used in chemical plants, power plants, cement plants, lime plants, coking plants, and high-temperature flue and hot air filtration in electric arc furnaces, oil boilers, incinerators, etc.
Mechanical and industrial applications
Aramid fiber has excellent mechanical properties and is widely used to manufacture various mechanical parts. For example, it can be used as a high-strength timing belt, transmission belt, pump diaphragm, and bearing material.
Its excellent wear resistance, high modulus, and high-temperature resistance make it an ideal material for manufacturing mechanical parts.

Summary
Aramid fibers exhibit strength, modulus, heat resistance, and abrasion properties. Para-aramid and meta-aramid contain different molecular arrangements impacting varied performance traits.
Para-aramid possesses straight molecular alignment, granting high strength and stiffness applied in armor, cables, and seals. Meta-aramid’s zigzag configuration provides outstanding temperature tolerance in protective apparel, insulation, and filters.
Compared to carbon fiber and ultra-high polyethylene, aramid withstands greater heat while retaining elongation integrity. It replaces carbon fiber where reinforcement and resilience matter. Aramid also outperforms polyethylene in demanding protective applications.
Initially developed for aerospace and defense, aramid production grew commercial as technologies transitioned. DuPont established fiber commercialization that others continue.
Aramid diversifies roles across optoelectronics, construction, transportation, and industry through properties facilitating lightweight optimization, protection, reinforcement, and filtration.
FAQ
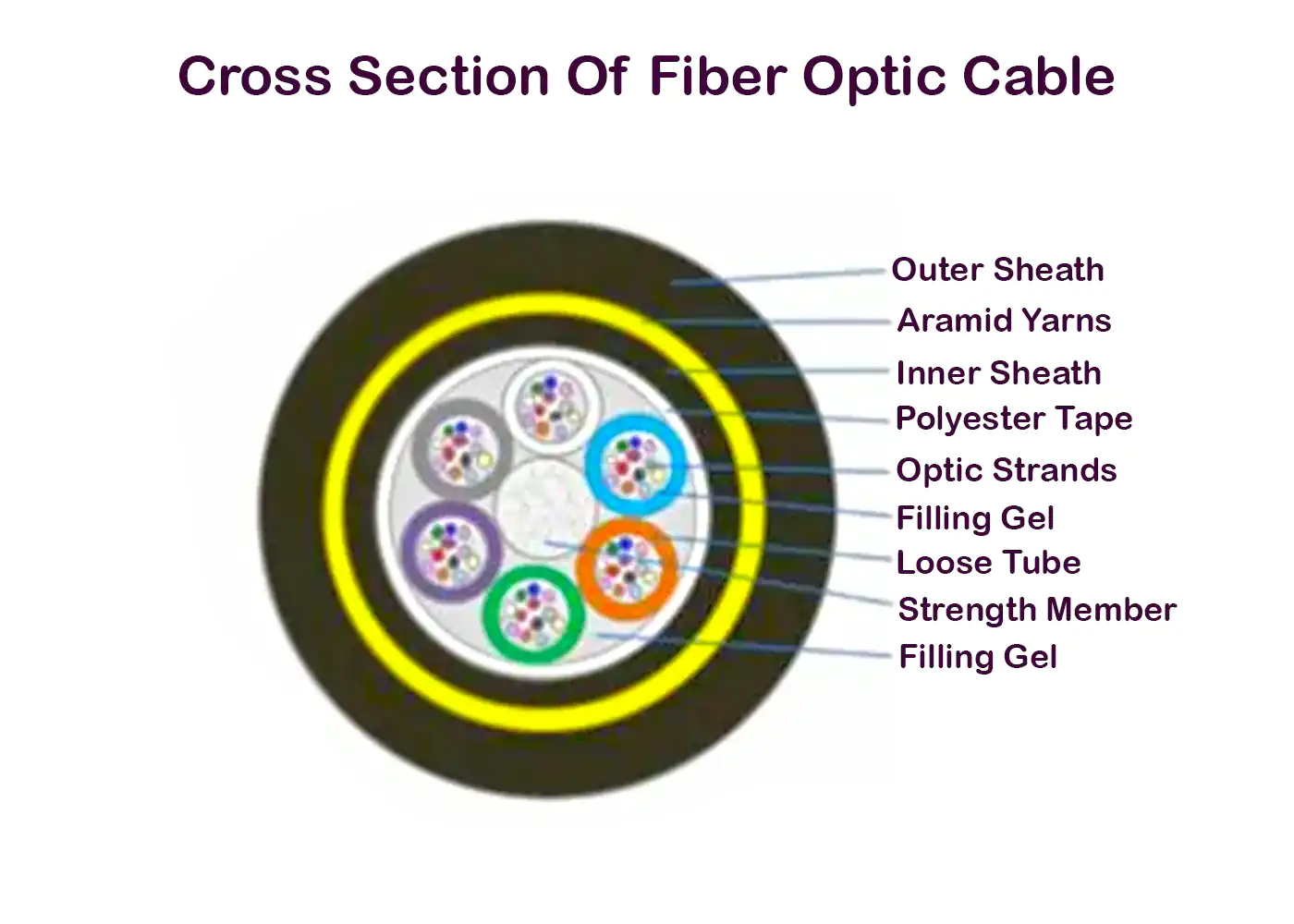
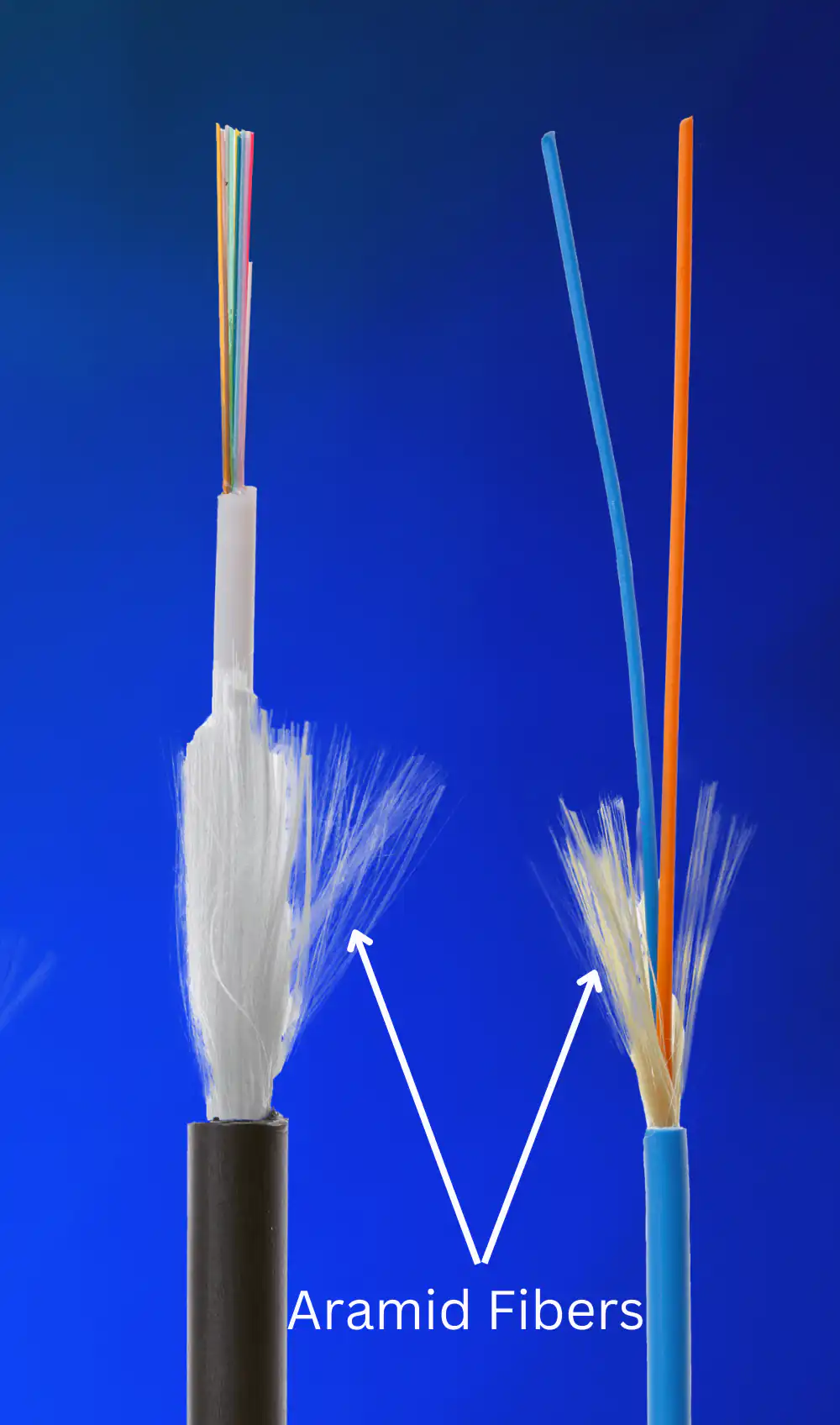
What is the aramid yarn or Kevlar layer for in a fiber optic cable?
Aramid yarn or Kevlar layer in a fiber optic cable provides strength and protection. Aramid yarn is a strong and lightweight synthetic fiber often used in applications requiring high strength, like bulletproof vests. Placed around the outside of the cable, it offers tensile strength, safeguarding the cable from damage caused by bending or twisting. The yarn also protects the cable from moisture and other environmental factors. Its benefits include superior strength, lightweight nature, and resistance to damage, making it an essential component for durable and reliable fiber optic cables.
Is aramid better than glass fiber?
A direct comparison between aramid and glass fibers is challenging since they serve different purposes in fiber optic cable production. Aramid fibers offer high stiffness, strength, and abrasion resistance and protect optical fibers from damage. Glass fibers, used as the core, ensure high optical clarity and low attenuation for transmitting light signals. Overall, each fiber type has unique properties suited for its specific roles in fiber optic cables.









VERY GOOD INFORMATION